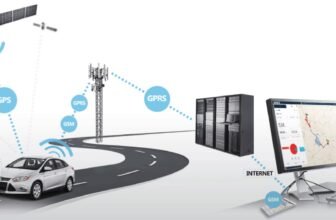
The Internet of Things and the Role of Satellites in Connecting the World
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how devices communicate, collect data, and interact with the world around us. From smart cities and automated industries to connected homes and precision agriculture, IoT is enabling efficiency, automation, and intelligence at unprecedented levels. However, for IoT to reach its full potential, seamless global connectivity is crucial. This is where satellites play a key role. As terrestrial networks struggle to cover remote, rural, and underserved areas, satellite-based IoT networks bridge this gap, ensuring that billions of devices worldwide remain connected.
The Growth of IoT and Its Connectivity Challenges
The IoT ecosystem is expanding rapidly. According to industry estimates, there will be over 50 billion connected devices by 2030, spanning industries such as healthcare, transportation, energy, and agriculture. These devices generate massive amounts of data that require robust and reliable connectivity. While terrestrial networks like fiber-optic cables and cellular towers provide coverage in urban and suburban areas, they fail to reach vast portions of the globe, including oceans, mountains, forests, and rural communities.
This limitation poses a challenge for industries that depend on real-time data and automation in remote locations, such as maritime logistics, mining operations, precision farming, and environmental monitoring. To achieve truly ubiquitous IoT coverage, a complementary solution is required—one that only satellite networks can provide.
How Satellites Enable Global IoT Connectivity
Satellites are uniquely positioned to support IoT connectivity worldwide. Unlike terrestrial networks, which require costly infrastructure development and maintenance, satellite networks can provide seamless coverage across the globe without geographical restrictions. These satellites operate in different orbits, including:
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): These satellites remain fixed relative to the Earth’s surface, providing continuous coverage over large areas. They are well-suited for applications requiring stable, high-bandwidth connections, such as weather monitoring and industrial IoT.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Positioned between GEO and Low Earth Orbit (LEO), MEO satellites provide a balance of coverage and low latency, making them suitable for applications like maritime and aviation IoT.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): LEO satellites are closer to the Earth’s surface, offering lower latency and high-speed connectivity. Companies like SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Project Kuiper are leveraging LEO satellites to provide global broadband access, which is crucial for IoT applications requiring real-time data transmission.
By deploying a network of interconnected satellites, IoT devices can communicate without relying solely on ground-based infrastructure. This approach ensures uninterrupted connectivity for industries operating in challenging environments.
Applications of Satellite-Enabled IoT
The integration of satellites and IoT is transforming multiple sectors, driving efficiency, security, and sustainability. Here are some key applications:
1. Smart Cities
Urban centers worldwide are evolving into smart cities, where connected sensors and devices enhance infrastructure and public services. Satellite IoT enables:
- Traffic and Transportation Management: Real-time GPS tracking, satellite imaging, and connected traffic signals reduce congestion and improve public transit efficiency.
- Environmental Monitoring: Satellites provide continuous data on air quality, noise pollution, and weather conditions, enabling proactive policy-making.
- Emergency Response: In disasters, satellite networks ensure first responders have uninterrupted connectivity, allowing for better coordination and rescue operations.
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industries such as oil and gas, mining, and manufacturing depend on remote monitoring and automation to optimize operations. Satellite IoT provides:
- Asset Tracking: Companies can monitor equipment and vehicles in real-time, reducing losses and improving logistics.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors connected via satellite detect potential machine failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Remote Operations: Automated drilling, mining, and manufacturing processes become more efficient with real-time satellite communication.
3. Agriculture and Environmental Sustainability
Precision agriculture is transforming food production, allowing farmers to maximize yield while minimizing resource consumption. Satellite IoT supports:
- Smart Irrigation: Sensors detect soil moisture levels and communicate with satellite systems to optimize water usage.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Satellites track vegetation indices, helping farmers detect diseases and optimize fertilization strategies.
- Livestock Tracking: GPS-enabled collars track animal movement and health, reducing losses and improving animal welfare.
4. Maritime and Aviation IoT
The vast oceans and skies lack consistent ground-based communication networks, making satellite connectivity essential. IoT solutions in these sectors include:
- Ship and Cargo Tracking: Real-time vessel tracking improves supply chain efficiency and safety.
- Weather Monitoring: Satellites provide critical weather data, helping airlines and shipping companies plan routes and avoid hazards.
- Passenger Connectivity: Satellite-enabled Wi-Fi enhances passenger experiences in flights and cruises.
5. Healthcare and Remote Medicine
Bridging the healthcare gap in rural and underserved regions is a significant challenge. Satellite IoT facilitates:
- Telemedicine: Doctors can diagnose and monitor patients remotely via satellite-connected medical devices.
- Disease Tracking: Global health organizations leverage IoT sensors and satellite imagery to track disease outbreaks in real time.
- Emergency Medical Response: Ambulances and medical evacuation helicopters use satellite IoT for navigation and real-time patient data transmission.
The Future of IoT and Satellite Integration
The future of satellite-enabled IoT is promising, with advancements in satellite technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and 5G networks enhancing connectivity. Several emerging trends will shape the landscape:
- 5G and Satellite Convergence: The integration of 5G with satellite networks will improve speed, reliability, and bandwidth for IoT applications.
- Edge Computing in Space: Satellites equipped with onboard AI will process IoT data closer to the source, reducing latency and optimizing efficiency.
- Energy-Efficient IoT Devices: The development of low-power IoT sensors will enable longer battery life and sustainability in remote environments.
- Affordable Satellite Services: As satellite launches become more cost-effective, more businesses and governments will leverage satellite IoT for diverse applications.
The Internet of Things is reshaping industries, cities, and everyday life, but its success depends on reliable global connectivity. Satellites play a critical role in bridging connectivity gaps, ensuring that IoT devices function seamlessly regardless of location. From smart cities and industries to agriculture, healthcare, and maritime logistics, satellite-enabled IoT is unlocking new possibilities, enhancing efficiency, and driving economic growth. As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between satellites and IoT will pave the way for a truly interconnected world, making the future smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable for all.