Does Satellite Internet Really Work?
Satellite internet has grown in popularity over the years, offering connectivity in areas where traditional broadband services might not be available. But does it truly deliver a reliable and effective online experience? Let’s delve into its functionality, compare its speed and price, discuss when it’s the right option, and guide you on how to acquire it.
How Satellite Internet Works
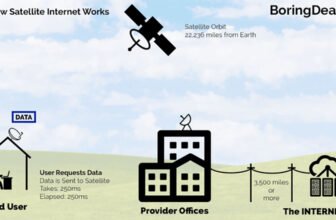
Satellite internet functions by transmitting data between a satellite orbiting the Earth and a satellite dish installed at the user’s location. The process involves:
- Data Request: A user sends a request (e.g., loading a webpage).
- Transmission to Satellite: The request is sent from the satellite dish to a satellite in geostationary orbit (around 22,000 miles above Earth).
- Transmission to Ground Station: The satellite relays the request to a ground station, which is connected to the broader internet.
- Response Path: The process is reversed to deliver the requested data back to the user.
While the technology is impressive, it’s worth noting that the long distances involved can lead to higher latency compared to terrestrial internet services.
Speed Comparison: Satellite Internet vs Other Options
Satellite internet speeds have improved significantly with advancements in technology. Providers like Starlink, Viasat, and HughesNet offer varying speeds, often depending on location and plan.
Satellite Internet Speeds
- Starlink: Offers speeds between 50 Mbps and 250 Mbps for standard plans, with lower latency than traditional satellite providers.
- Viasat: Provides speeds ranging from 12 Mbps to 100 Mbps, depending on the plan and region.
- HughesNet: Caps speeds at 25 Mbps but prioritizes reliability.
Comparison to Other Internet Types
- Fiber: Can reach speeds of 1 Gbps or higher with ultra-low latency, but is only available in urban and suburban areas.
- Cable: Typically offers speeds from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps with moderate latency.
- DSL: Ranges from 5 Mbps to 100 Mbps depending on distance from the provider’s infrastructure.
While satellite internet’s speeds can compete with DSL in some cases, its latency (often 20-50 milliseconds for Starlink or 600+ milliseconds for traditional providers) makes it less suitable for real-time applications like online gaming.
Pricing
Satellite internet pricing varies based on the provider, plan, and equipment fees:
- Starlink: Costs $120/month for residential service, with a one-time equipment fee of $599. Additional plans like Starlink Roam cater to users who need connectivity on the go.
- Viasat: Plans start around $49.99/month for basic packages and can go up to $150+/month for higher-speed options.
- HughesNet: Offers plans starting at $64.99/month, with data caps ranging from 15 GB to 75 GB.
While satellite internet is often more expensive than fiber or cable, it provides a critical solution for rural and remote areas where other options are unavailable.
When Should You Consider Satellite Internet?
Satellite internet is ideal if:
- You Live in a Remote Area: Traditional broadband services might not reach your location.
- You Need Internet on the Move: Certain satellite providers cater to RVs, boats, and other mobile setups.
- Other Options Are Inadequate: If DSL or mobile data services are too slow or unreliable, satellite internet can be a better alternative.
However, if fiber or cable is available in your area, these options often provide faster, more reliable, and cost-effective internet service.
How to Get Satellite Internet
Follow these steps to set up satellite internet at your location:
- Research Providers: Check availability in your area. Popular options include:
- Compare Plans: Evaluate speeds, data caps, and pricing to find the best fit for your needs.
- Order Equipment: Most providers require you to purchase or lease a satellite dish and modem.
- Professional Installation: Schedule an installation to ensure optimal dish placement and alignment.
- Activate Service: Follow the provider’s instructions to activate your connection.
Satellite internet is a viable solution for many, especially in areas with limited connectivity options. While it has limitations such as latency and higher costs, advancements like Starlink are bridging the gap between satellite and terrestrial internet services. By carefully assessing your needs and comparing providers, you can decide if satellite internet is the right choice for you.
For more information, visit the official websites of Starlink, Viasat, and HughesNet. image/wikimedia